Why 70% of Allergies Are Gut-Related
Western Medical Perspective: The Gut-Brain-Immune Axis
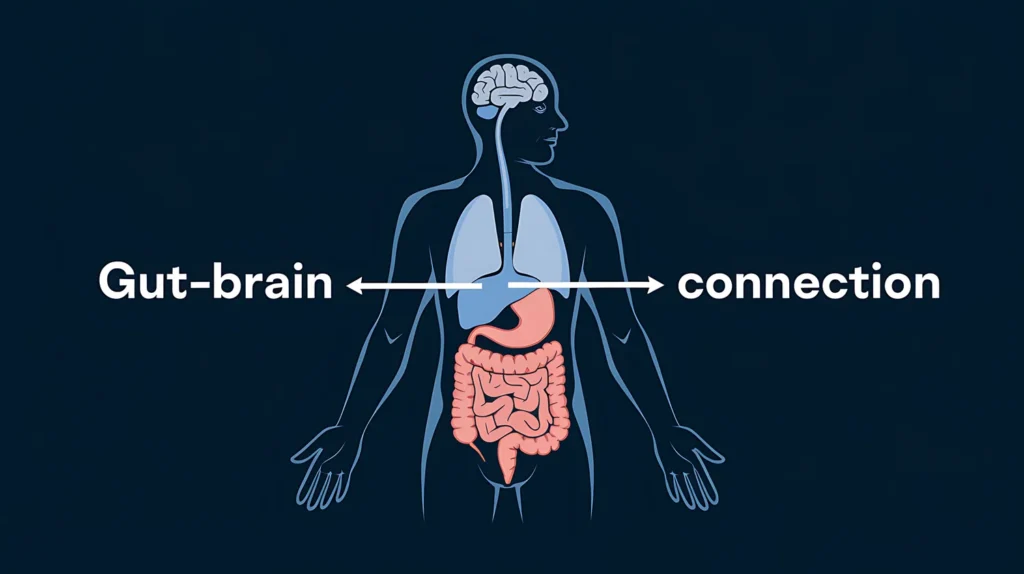
In Western medicine, the relationship between the gut and allergies is primarily understood through the concept of the gut-brain-immune axis. The gastrointestinal system plays a pivotal role in immune system regulation, with approximately, the body’s immune cells residing in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). Dysbiosis, or imbalance in the gut microbiota, can lead to increased intestinal permeability, often referred to as “leaky gut,” allowing allergens to translocate into the bloodstream and trigger systemic allergic responses.
Furthermore, the gut microbiota influences the development and function of immune cells, including regulatory T cells (Tregs) and IgA-producing plasma cells, which are crucial for maintaining immune tolerance. Disruptions in microbial diversity and function can impair these mechanisms, predisposing individuals to allergic conditions such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, and food allergies.
The Relationship Between the Digestive System and Allergies
The Gut: The Largest Immune Organ
Over 70% of the body’s immune cells are concentrated in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), including Peyer’s patches and mesenteric lymph nodes.
Impaired Gut Barrier Function
When the intestinal mucosal barrier is compromised such as in inflammatory bowel disease, leaky gut, or chronic digestive disorders more foreign antigens can enter the bloodstream directly. This can stimulate B cells to overproduce IgE or other abnormal antibodies, increasing the risk of allergic reactions.
Influence of the Microbiome
A healthy gut microbiota helps induce immune tolerance. When the microbiome is imbalanced (dysbiosis), the body is more likely to treat harmless substances as “enemies,” triggering allergic responses.
Clinical Evidence
Patients with digestive system disorders such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) often have a higher prevalence of food allergies, skin allergies, or asthma.
TCM Views on Allergies
In TCM, allergies are seen as the result of an imbalance in the body’s Qi, Yin, Yang, or Blood. Allergies are typically viewed as a form of external pathogenic invasion, particularly the invasion of Wind, Heat, Dampness, or Cold into the body. This invasion disrupts the body’s Defensive Qi (Wei Qi), which leads to the overreaction of the immune system.
Additionally, Wei Qi, the body’s defensive energy, is closely related to the Spleen’s function. A weakened Spleen fails to produce sufficient Qi, leading to compromised Wei Qi and increased susceptibility to allergens. TCM emphasizes the importance of strengthening the Spleen and resolving Dampness to restore balance and prevent allergic reactions.
Acupuncture and Herbal Medicine: Integrative Treatment Approaches
Acupuncture and herbal medicine are fundamental components of TCM in treating allergies by addressing the root causes:
- Acupuncture: Specific acupoints are selected to tonify Spleen Qi, resolve Dampness, and strengthen Wei Qi. Commonly used points include:
- ST36 (Zusanli): Strengthens the Spleen and Stomach, boosts Qi.
- SP6 (Sanyinjiao): Regulates the Spleen and Stomach, resolves Dampness.
- BL20 (Pishu): Tonifies the Spleen, harmonizes the middle Jiao.
- DU14 (Dazhui): Expels Wind, strengthens Wei Qi.
- Herbal Medicine: Herbs or Formulas are tailored to individual who suffer from complicated symptoms, but often need to be Modified alright:
- Shen Ling Bai Zhu San: Tonifies Spleen Qi and resolves Dampness.
- Yu Ping Feng San: Augments Qi and stabilizes the exterior.
- Allergy Ease is new porch that integrates traditional elements with modern research to address the needs of contemporary society for Allergies from Sol Nutrition.
Clinically Proven Benefits:
- Provides relief from: food, seasonal, & pet allergies*
- Helps combat sneezing, runny nose & itchy throat & eyes*
- Helps regulate antibody response to minimize histamine release and allergic reactions*
- Aids in modulating itchy skin due to an allergic reaction*
- Helps reduce excess IgE antibodies that trigger allergic reactions to food, pets, and seasonal allergens
- Pairs well with Immune Defense to build a strong immune system due to any allergies*
- Pairs well with Belly Reset for any gut allergy issues*
Dietary Considerations for Allergies
Dietary Recommendations in TCM
- Avoid Damp and Cold Foods: Foods like dairy, greasy or fried foods, and cold beverages can worsen Dampness and cause mucus buildup, exacerbating allergy symptoms.
- Warm and Spicy Foods: These foods help dispel Wind and Heat from the body, reducing allergic reactions. Examples include ginger, garlic, onions, and cinnamon.
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Foods rich in antioxidants and Omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and leafy greens, can help reduce the inflammation associated with allergies.
Specific Foods for Supporting Respiratory Health
- Radish: Helps to resolve phlegm and Dampness, beneficial for respiratory issues like sinusitis and asthma.
- Goji Berries: Nourish Yin and improve immune function, reducing sensitivity to allergens.
- Mushrooms: Shiitake and reishi mushrooms strengthen immunity and can help the body fight off allergic reactions.
Foods to Avoid
- Dairy Products: Often worsen sinus congestion and mucus production.
- Wheat and Gluten: Can exacerbate inflammation and allergic responses in sensitive individuals.
- Excessively Sweet Foods: Can create Dampness and worsen respiratory issues.
Conclusion: Supporting Your Immune Health
If you have been diagnosed with allergies or are experiencing allergy symptoms, it is important to seek proper evaluation and testing to identify the specific triggers. In addition to medical treatment, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential.
Focus on balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, Acupuncture and herbale formula as these factors are critical for supporting your immune defense. With healthy habits, you can help your body better manage allergic reactions and improve overall well-being.


